


Next: Performance Evaluation of Radix Sort
Up: Parallel Integer Sorting
Previous: Counting Sort Algorithm
Radix Sort makes several passes of the previous Counting Sort in
order to completely sort integer keys. Counting Sort can be used as
the intermediate sorting routine because it provides a stable sort.
Let the n integer keys fall in the range 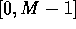 , and
, and 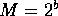 .
Then we need
.
Then we need  passes of Counting Sort; each pass works on
r-bit blocks of the input keys, starting from the least significant
block of r bits to the most significant block. Therefore, the
overall complexity of Radix Sort is exactly
passes of Counting Sort; each pass works on
r-bit blocks of the input keys, starting from the least significant
block of r bits to the most significant block. Therefore, the
overall complexity of Radix Sort is exactly  times that
of Counting Sort. We choose the radix R to be
times that
of Counting Sort. We choose the radix R to be 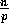 (note
that we are assuming
(note
that we are assuming 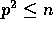 ), and a typical value is R=1024.
Assuming that M is polynomial in n,
), and a typical value is R=1024.
Assuming that M is polynomial in n,  becomes a
constant, and therefore, the total complexity reduces to
becomes a
constant, and therefore, the total complexity reduces to 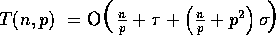 . Thus, the computational
analysis derived for radix sort is asymptotically optimal since
sequential radix sort runs in
. Thus, the computational
analysis derived for radix sort is asymptotically optimal since
sequential radix sort runs in 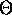
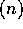 whenever the range of integers
is polynomial in n. The lower bound for communication is
whenever the range of integers
is polynomial in n. The lower bound for communication is 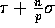 since each processor might need to inject all of
its elements into the network, and the communication complexity is
asymptotically optimal whenever
since each processor might need to inject all of
its elements into the network, and the communication complexity is
asymptotically optimal whenever 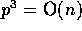 .
.



Next: Performance Evaluation of Radix Sort
Up: Parallel Integer Sorting
Previous: Counting Sort Algorithm
David A. Bader
dbader@umiacs.umd.edu
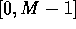 , and
, and 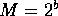 .
Then we need
.
Then we need  passes of Counting Sort; each pass works on
r-bit blocks of the input keys, starting from the least significant
block of r bits to the most significant block. Therefore, the
overall complexity of Radix Sort is exactly
passes of Counting Sort; each pass works on
r-bit blocks of the input keys, starting from the least significant
block of r bits to the most significant block. Therefore, the
overall complexity of Radix Sort is exactly  times that
of Counting Sort. We choose the radix R to be
times that
of Counting Sort. We choose the radix R to be 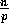 (note
that we are assuming
(note
that we are assuming 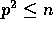 ), and a typical value is R=1024.
Assuming that M is polynomial in n,
), and a typical value is R=1024.
Assuming that M is polynomial in n,  becomes a
constant, and therefore, the total complexity reduces to
becomes a
constant, and therefore, the total complexity reduces to 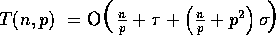 . Thus, the computational
analysis derived for radix sort is asymptotically optimal since
sequential radix sort runs in
. Thus, the computational
analysis derived for radix sort is asymptotically optimal since
sequential radix sort runs in 
 whenever the range of integers
is polynomial in n. The lower bound for communication is
whenever the range of integers
is polynomial in n. The lower bound for communication is 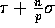 since each processor might need to inject all of
its elements into the network, and the communication complexity is
asymptotically optimal whenever
since each processor might need to inject all of
its elements into the network, and the communication complexity is
asymptotically optimal whenever 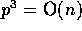 .
.